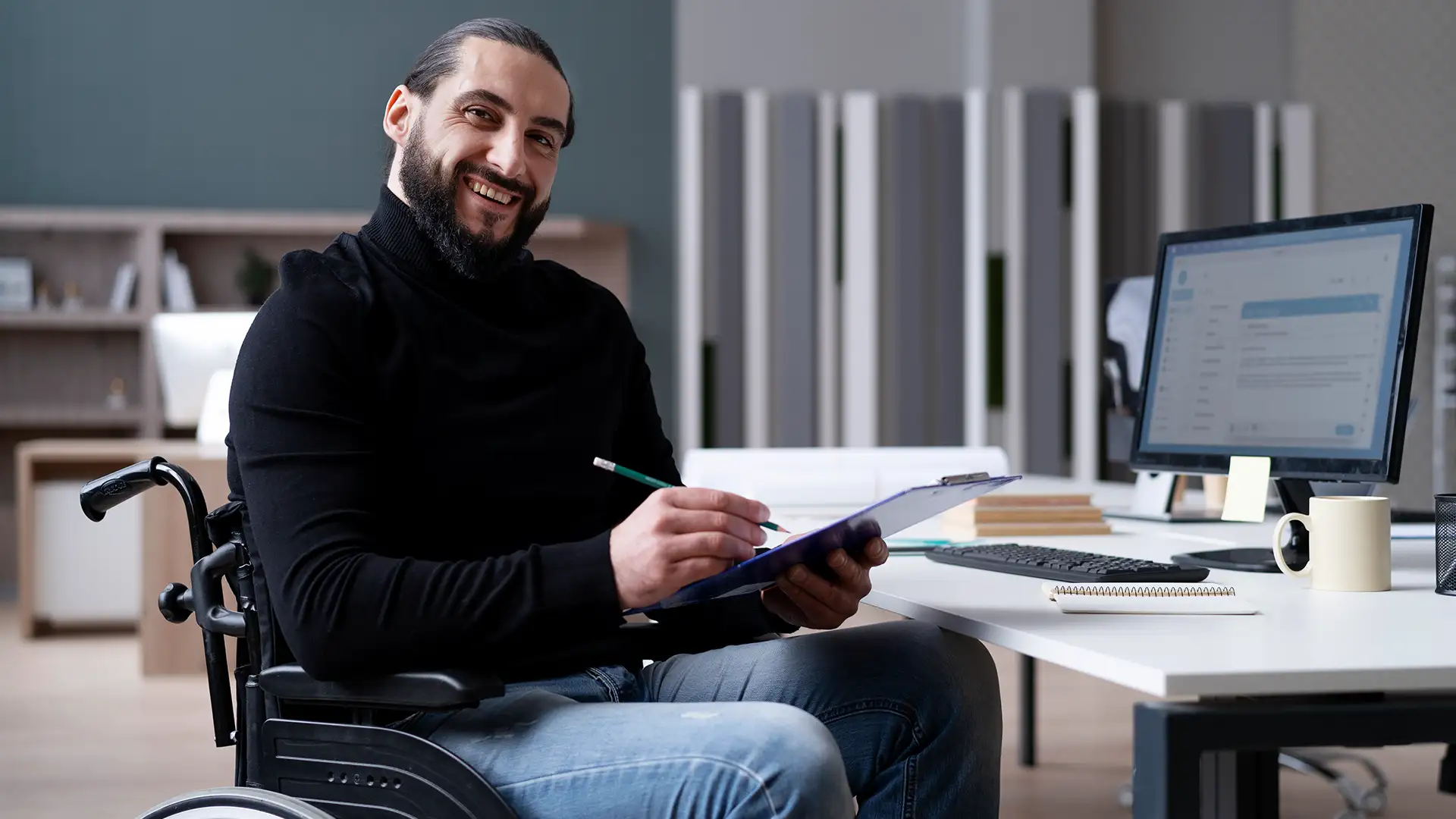
ADA compliance in the business world refers to adherence to the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), a U.S. federal law that prohibits discrimination against individuals with disabilities. The ADA was enacted in 1990 with the aim of ensuring equal opportunities and access for people with disabilities in various areas of public life, including employment, public services, and businesses. ADA compliance is crucial for creating inclusive environments and ensuring that individuals with disabilities have equal access to goods, services, and facilities.
In the business context, ADA compliance covers several aspects:
Physical Accessibility:
Businesses are required to ensure that their physical spaces are accessible to individuals with disabilities. This includes providing ramps, accessible entrances, parking spaces, and other accommodations to facilitate mobility.
Accessible Communication:
Businesses must ensure that their communication methods are accessible to individuals with disabilities. This may involve providing alternative formats for written materials, ensuring that websites are accessible to people with visual or auditory impairments, and offering auxiliary aids and services, such as sign language interpreters, for effective communication.

Employment Practices:
ADA compliance extends to employment practices. Employers are required to provide reasonable accommodation to qualified employees with disabilities, allowing them to perform essential job functions. This may include modifications to workspaces, flexible schedules, or the use of assistive technology.
Goods and Services:
Businesses offering goods and services to the public must ensure that individuals with disabilities have equal access. This includes accessible facilities, accommodations in service delivery, and accessible information about products or services.
Digital Accessibility:
With the increasing reliance on digital platforms, businesses are also expected to ensure that their websites, applications, and other digital content are accessible to individuals with disabilities. This involves designing websites in a way that accommodates screen readers, providing text alternatives for non-text content, and ensuring compatibility with assistive technologies.
Training and Awareness:
Businesses are encouraged to provide training for employees to raise awareness about ADA requirements and promote a culture of inclusivity. This includes educating staff about the rights of individuals with disabilities and the importance of making accommodation.
Non-compliance with ADA regulations can result in legal consequences, including fines and potential lawsuits. Therefore, businesses often engage in proactive measures to assess and improve their ADA compliance, working to create environments that are accessible and welcoming to individuals of all abilities. It’s important to note that similar principles of accessibility and inclusion are recognized and implemented in various countries worldwide, although the specific legal requirements may vary.





































Leave a Reply